Roman province
This article needs better sources. (January 2025) |
| History of geography |
|---|
 |
 |
|---|
| Periods |
|
| Constitution |
| Political institutions |
| Assemblies |
| Ordinary magistrates |
| Extraordinary magistrates |
| Public law |
| Senatus consultum ultimum |
| Titles and honours |
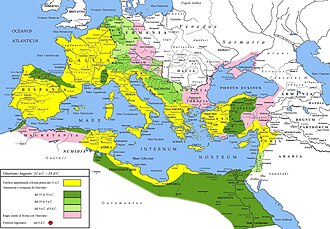

The Roman provinces (Latin: provincia, pl. provinciae) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as governor.[1][better source needed]
For centuries, it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome.[1] With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the imperial prefectures).[1]
History
[edit]A province was the basic and, until the Tetrarchy (from AD 293), the largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside Roman Italy.
During the republic and early empire, provinces were generally governed by politicians of senatorial rank, usually former consuls or former praetors.[1] A later exception was the province of Egypt, which was incorporated by Augustus after the death of Cleopatra and was ruled by a governor of only equestrian rank, perhaps as a discouragement to senatorial ambition.[1] That exception was unique but not contrary to Roman law, as Egypt was considered Augustus's personal property, following the tradition of the kings of the earlier Hellenistic period.[1]
Republican period
[edit]The English word province comes from the Latin word provincia.[2] The Latin term provincia had an equivalent in eastern, Greek-speaking parts of the Greco-Roman world. In the Greek language, a province was called an eparchy (Greek: ἐπαρχίᾱ, eparchia), with a governor called an eparch (Greek: ἔπαρχος, eparchos).[3]
Emergence
[edit]The Latin provincia, during the middle republic, referred not to a territory, but to a task assigned to a Roman magistrate. That task might require using the military command powers of imperium but otherwise could even be a task assigned to a junior magistrates without imperium: for example, the treasury was the provincia of a quaestor and the civil jurisdiction of the urban praetor was the urbana provincia.[2] In the middle and late republican authors like Plautus, Terence, and Cicero, the word referred something akin to a modern ministerial portfolio:[4] "when... the senate assigned provinciae to the various magistrates... what they were doing was more like allocating a portfolio than putting people in charge of geographic areas".[5]
The first commanders dispatched with provinciae were for the purpose of waging war and to command an army. However, merely that a provincia was assigned did not mean the Romans made that territory theirs. For example, Publius Sulpicius Galba Maximus in 211 BC received Macedonia as his provincia but the republic did not annex the kingdom, even as Macedonia was continuously assigned until 205 BC with the end of the First Macedonian War. Even though the Second and Third Macedonian Wars saw the Macedonian province revived, the senate settled affairs in the region by abolishing Macedonia and replacing it with four client republics. Macedonia only came under direct Roman administration in the aftermath of the Fourth Macedonian War in 148 BC.[6] Similarly, assignment of various provinciae in Hispania was not accompanied by the creation of any regular administration of the area; indeed, even though two praetors were assigned to Hispania regularly from 196 BC, no systematic settlement of the region occurred for nearly thirty years and what administration occurred was ad hoc and emerged from military necessities.[7]
In the middle republic, the administration of a territory – whether taxation or jurisdictrion – had basically no relationship with whether that place was assigned as a provincia by the senate. Rome would even intervene on territorial disputes which were part of no provincia at all and were not administered by Rome.[8] The territorial province, called a "permanent" provincia in the scholarship, emerged only gradually.
Permanent provincia
[edit]The acquisition of territories, however, through the middle republic created the recurrent task of defending and administering some place. The first "permanent" provincia was that of Sicily, created after the First Punic War. In the immediate aftermath, a quaestor was sent to Sicily to look out for Roman interests but eventually, praetors were dispatched as well. The sources differ as to when sending a praetor became normal: Appian reports 241 BC; Solinus indicates 227 BC instead. Regardless, the change likely reflected Roman unease about Carthaginian power: quaestors could not command armies or fleets; praetors could and initially seem to have held largely garrison duties.[9] This first province started a permanent shift in Roman thinking about provincia. Instead of being a task of military expansion, it became a recurrent defensive assignment to oversee conquered territories. These defensive assignments, with few opportunities to gain glory, were less desirable and therefore became regularly assigned to the praetors.[10]
Only around 180 BC did provinces take on a more geographically defined position when a border was established to separate the two commanders assigned to Hispania on the river Baetis.[11] Later provinces, once campaigns were complete, were all largely defined geographically.[12] Once this division of permanent and temporary provinciae emerged, magistrates assigned to permanent provinces also came under pressures to achieve as much as possible during their terms. Whenever a military crisis occurred near some province, it was normally reassigned to one of the consuls; praetors were left with the garrison duties.[13] In the permanent provinces, the Roman commanders were initially not intended as administrators. However, the presence of the commander with forces sufficient to coerce compliance made him an obvious place to seek final judgement. A governor's legal jurisdiction thus grew from the demands of the provincial inhabitants for authoritative settlement of disputes.[14]
In the absence of opportunities for conquest and with little oversight for their activities, many praetorian governors settled on extorting the provincials. This profiteering threatened Roman control by unnecessarily angering the province's subject populations and was regardless dishonourable. It eventually drew a reaction from the senate, which reacted with laws to rein in the governors.[15] After initial experimentation with ad hoc panels of inquest, various laws were passed, such as the lex Calpurnia de repetundis in 149 BC, which established a permanent court to try corruption cases; troubles with corruption and laws reacting to it continued through the republican era.[16] By the end of the republic, a multitude of laws had been passed on how a governor would complete his task, requiring presence in the province, regulating how he could requisition goods from provincial communities, limiting the number of years he could serve in the province, etc.[17]
Assignment
[edit]Prior to 123 BC, the senate assigned consular provinces as it wished, usually in its first meeting of the consular year. The specific provinces to be assigned were normally determined by lot or by mutual agreement among the commanders; only extraordinarily did the senate assign a command extra sortem (outside of sortition).[18] But in 123 or 122 BC, the tribune Gaius Sempronius Gracchus passed the lex Sempronia de provinciis consularibus, which required the senate to select the consular provinces before the consular elections and made this announcement immune from tribunician veto.[19] The law had the effect of, over time, abolishing the temporary provinciae, as it was not always realistic for the senate to anticipate the theatres of war some six months in advance. Instead, the senate chose to assign consuls to permanent provinces near expected trouble spots. From 200 to 124 BC, only 22 per cent of recorded consular provinciae were permanent provinces; between 122 and 53 BC, this rose to 60 per cent.[20]
While many of the provinces had been assigned to sitting praetors in the earlier part of the second century, with new praetorships created to fill empty provincial commands, by the start of the first century it had become uncommon for praetors to hold provincial commands during their formal annual term. Instead they generally took command as promagistrate after the end of their term. The use of prorogation was due to an insufficient number of praetors, which was for two reasons: more provinces needed commands[21] and the increased number of permanent jury courts (quaestiones perpetuae), each of which had a praetor as president, exacerbated this issue.[22] Praetors during the second century were normally prorogued pro praetore, but starting with the Spanish provinces and expanding by 167 BC, praetors were more commonly prorogued with the augmented rank pro consule; by the end of the republic, all governors acted pro consule.[23]
Also important was the assertion of popular authority over the assignment of provincial commands. This started with Gaius Marius, who had an allied tribune introduce a law transferring to him the already-taken province of Numidia (then held by Quintus Caecilius Metellus), allowing Marius to assume command of the Jugurthine War.[24] This innovation destabilised the system of assigning provincial commands, exacerbated internal political tensions, and later allowed ambitious politicians to assemble for themselves enormous commands which the senate would never have approved: the Pompeian lex Gabinia of 67 BC granted Pompey all land within 50 miles of the Mediterranean; Caesar's Gallic command that encompassed three normal provinces.[25]
Late Republican period
[edit]In the late Republican period, Roman authorities generally preferred that a majority of people in Rome's provinces venerated, respected, and worshipped gods from Rome proper and Roman Italy to an extent, alongside normal services done in honor of their "traditional" gods.[26]
Transition to empire
[edit]The increasing practices of prorogation and statutorily-defined "super commands" driven by popularis political tactics[27] undermined the republican constitutional principle of annually-elected magistracies. This allowed the powerful men to amass disproportionate wealth and military power through their provincial commands, which was one of the major factors in the transition from a republic to an imperial autocracy.[28][29][30][31][32]
The senate attempted to push back against these commands in many instances: it preferred to break up any large war into multiple territorially separated commands; for similar reasons, it opposed the lex Gabinia which gave Pompey an overlapping command over large portions of the Mediterranean.[33] The senate, which had long acted as a check on aristocratic ambitions, was unable to stop these immense commands, which culminated eventually with the reduction of the number of meaningfully-independent governors during the triumviral period to three men and, with the end of the republic, to one man.
Early imperial period
[edit]During his sixth and seventh consulships (28 and 27 BC), Augustus began a process which saw the republic return to "normality": he shared the fasces that year with his consular colleague month-by-month and announced the abolition of the triumvirate by the end of the year in accordance with promises to do so at the close of the civil wars.[34] At the start of 27 BC, Augustus formally had a provincial command over all of Rome's provinces. That year, in his "first settlement", he ostentatiously returned his control of them and their attached armies to the senate, likely by declaring that the task assigned to him either by the lex Titia creating the Triumvirate or that the war on Cleopatra and Antony was complete.[35] In return, at a carefully-managed meeting of the senate, he was given commands over Spain, Gaul, Syria, Cilicia, Cyprus, and Egypt to hold for ten years; these provinces contained 22 of the 28 extant Roman legions (over 80 per cent) and contained all prospective military theatres.[36]
The provinces that were assigned to Augustus became known as imperial provinces and the remaining provinces, largely demilitarised and confined to the older republican conquests, became known as public or senatorial provinces, as their commanders were still assigned by the senate on an annual basis consistent with tradition.[37] Because no one man could command in practically all the border-regions of the empire at once, Augustus appointed subordinate legates for each of the provinces with the title legatus Augusti pro praetore. These lieutenant legati probably held imperium but, due to their lack of an independent command, were unable to triumph and could be replaced by their superior (Augustus) at any time.[38] These arrangements were likely based on the precedent of Pompey's proconsulship over the Spanish provinces after 55 BC entirely through legates, while he stayed in the vicinity of Rome.[39][40] In contrast, the public provinces continued to be governed by proconsuls with formally independent commands.[37] In only three of the public provinces were there any armies: Africa, Illyricum, and Macedonia; after Augustus' Balkan wars, only Africa retained a legion.[41]
To make this monopolisation of military commands palatable, Augustus separated prestige from military importance and inverted it. The title pro praetore had gone out of use by the end of the republic and was regardless in inferior status to a proconsul. More radically, Egypt (which was sufficiently powerful that a commander there could start a rebellion against the emperor) was commanded by an equestrian prefect, "a very low title indeed" as prefects were normally low-ranking officers and equestrians were not normally part of the elite.[42] In Augustus' "second settlement" of 23 BC, he gave up his continual holding of the consulship in exchange for a general proconsulship – with a special dispensation from the law that nullified imperium within the city of Rome – over the imperial provinces.[43] He also gave himself, through the senate, a general grant of imperium maius, which gave him priority over the ordinary governors of the public provinces, allowing him to interfere in their affairs.[44]
Within the public and imperial provinces there also existed distinctions of rank. In the public provinces, the provinces of Africa and Asia were given only to ex-consuls; ex-praetors received the others. The imperial provinces eventually produced a three-tier system with prefects and procurators, legates pro praetore who were ex-praetors, and legates pro praetore who were ex-consuls.[45] The public provinces' governors normally served only one year; the imperial provinces' governors on the other hand normally served several years before rotating out.[46] The extent to which the emperor exercised control over all the provinces increased during the imperial period: Tiberius, for example, once reprimanded legates in the imperial provinces for failing to forward financial reports to the senate; by the reign of Claudius, however, the senatorial provinces' proconsuls were regularly issued with orders directly from the emperor.[47]
Late imperial period
[edit]
The emperor Diocletian introduced a radical reform known as the tetrarchy (AD 284–305), with a western and an eastern senior emperor styled Augustus, each seconded by a junior emperor (and designated successor) styled caesar.[1] Each of these four defended and administered a quarter of the empire. In the 290s, Diocletian divided the empire anew into almost a hundred provinces, including Roman Italy.[1] Their governors were hierarchically ranked, from the proconsuls of Africa Proconsularis and Asia through those governed by consulares and correctores to the praesides. The provinces in turn were grouped into (originally twelve) dioceses, headed usually by a vicarius, who oversaw their affairs. Only the proconsuls and the urban prefect of Rome (and later Constantinople) were exempt from this, and were directly subordinated to the tetrarchs.[1]
Although the Caesars were soon eliminated from the picture, the four administrative resorts were restored in 318 by Emperor Constantine I, in the form of praetorian prefectures, whose holders generally rotated frequently, as in the usual magistracies but without a colleague.[1] Constantine also created a new capital, named after him as Constantinople, which was sometimes called 'New Rome' because it became the permanent seat of the government.[1] In Italy itself, Rome had not been the imperial residence for some time and 286 Diocletian formally moved the seat of government to Mediolanum (modern Milan), while taking up residence himself in Nicomedia.[1] During the 4th century, the administrative structure was modified several times, including repeated experiments with Eastern-Western co-emperors.[48]

Detailed information on the arrangements during this period is contained in the Notitia Dignitatum (Record of Offices), a document dating from the early 5th century. Most data is drawn from this authentic imperial source, as the names of the areas governed and titles of the governors are given there. There are however debates about the source of some data recorded in the Notitia, and it seems clear that some of its own sources are earlier than others. Some scholars compare this with the list of military territories under the duces, in charge of border garrisons on so-called limites, and the higher ranking Comites rei militaris, with more mobile forces, and the later, even higher magistri militum.[49]
Justinian I made the next great changes in 534–536 by abolishing, in some provinces, the strict separation of civil and military authority that Diocletian had established.[1]This process was continued on a larger scale with the creation of extraordinary Exarchates in the 580s and culminated with the adoption of the military theme system in the 640s, which replaced the older administrative arrangements entirely.[1] Some scholars use the reorganization of the empire into themata in this period as one of the demarcations between the Dominate and the Byzantine (or the Later Roman) period.[citation needed]
List of provinces
[edit]Republican provinces
[edit]| Year | Province | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 241 BC | Sicilia (Sicily) | Taken over from the Carthaginians and annexed at the end of the First Punic War. |
| 237 BC | Sardinia and Corsica | Taken over from the Carthaginians and annexed soon after the Mercenary War, in 238 BC and 237 BC respectively. |
| 197 BC | Hispania Citerior | Along the east coast of the Iberian Peninsula; part of the territories taken over from the Carthaginians. |
| 197 BC | Hispania Ulterior | Along the southern coast of the Iberian Peninsula; part of the territories taken over from the Carthaginians in the Second Punic War. |
| 147 BC | Macedonia | Annexed after the Achaean War. |
| 146 BC | Africa | Modern-day Tunisia, eastern Algeria, and western Libya; created after the destruction of Carthage in the Third Punic War. |
| 129 BC | Asia | Formerly the Attalid kingdom, in western Anatolia (now in Turkey), bequeathed to Rome by its last king, Attalus III, in 133 BC. |
| 120 BC | Gallia Narbonensis | Southern France; previously called Gallia Transalpina to distinguish it from Gallia Cisalpina. Annexed following attacks on the allied Greek city of Massalia (Marseille). |
| 67 BC | Crete and Cyrenaica | Cyrenaica was bequeathed to Rome in 78 BC but not organised as a province until Crete was annexed in 66 BC. |
| 63 BC | Bithynia et Pontus | The Kingdom of Bithynia was bequeathed to Rome by its last king, Nicomedes IV, in 74 BC. Organised as a Roman province at the end of the Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC) by Pompey, incorporating the western part of the defeated Kingdom of Pontus in 63 BC. |
| 63 BC | Syria | Created by Pompey after deposing the last Seleucid king Philip II Philoromaeus. |
| 63 BC | Cilicia | Initially created as a military command area in 102 BC during a campaign against piracy. Fully came under Roman control at the end of the Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), reorganised by Pompey in 63 BC. |
| 58 BC | Cyprus | Annexed after the death of its last king Ptolemy of Cyprus and added to the province of Cilicia, creating the province of Cilicia et Cyprus. |
| 46 BC | Africa Nova | Eastern Numidia annexed by Julius Caesar and named Africa Nova (new Africa) to distinguish it from Africa Vetus (old Africa). Western Numidia was added to Africa Nova in 40 BC. |
Cisalpine Gaul (in northern Italy) was occupied by Rome in the 220s BC and became considered geographically and de facto part of Roman Italy,[50] but remained politically and de jure separated. It was legally merged into the administrative unit of Roman Italy in 42 BC by the triumvir Augustus as a ratification of Caesar's unpublished acts (Acta Caesaris).[51][52][53][54][55]
Provinces of the Principate
[edit]| Year | Province | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Under Augustus | ||
| 30 BC | Aegyptus | Taken over by Augustus after the defeat of Mark Antony and Cleopatra VII. Governed by Augustus' praefectus, Alexandreae et Aegypti. |
| 27 BC | Achaia | Augustus separated it from Macedonia. |
| 27 BC | Hispania Tarraconensis | Former Hispania Citerior reorganized by Augustus (imperial proconsular province). |
| 27 BC | Lusitania | Created by Augustus in the reorganization of Hispania (imperial proconsular province). |
| 27 BC | Illyricum | Initially senatorial, became imperial in 11 BC. Later divided into Dalmatia and Pannonia. |
| 27 BC or 16–13 BC | Aquitania | Created in territories conquered by Julius Caesar (imperial proconsular province). |
| 27 BC or 16–13 BC | Gallia Lugdunensis | Created in territories conquered by Julius Caesar (imperial proconsular province). |
| 25 BC | Galatia | Annexed after the death of its last king Amyntas. |
| 25 BC | Africa Proconsularis | Merged Africa Nova and Africa Vetus. |
| 22 BC | Gallia Belgica | Created in territories of Gaul (imperial proconsular province). |
| 15 BC | Raetia | Imperial procuratorial province. |
| 14 BC | Hispania Baetica | Former Hispania Ulterior reorganized by Augustus (senatorial propraetorial province). |
| 7 BC | Germania Antiqua | Lost after the defeat in 9 AD. |
| AD 6 | Moesia | Initially a military district, became a province in AD 6. |
| AD 6 | Judaea | Created after the deposition of Herod Archelaus. |
| Under Tiberius | ||
| AD 17 | Cappadocia | Created after the death of its last king Archelaus. |
| Under Claudius | ||
| AD 42 | Mauretania Tingitana | Annexed and divided after the death of Ptolemy. |
| AD 42 | Mauretania Caesariensis | Annexed and divided after the death of Ptolemy. |
| AD 41/53 | Noricum | Became a proper province during Claudius' reign. |
| AD 43 | Britannia | Conquered by Claudius, divided into Britannia Superior and Britannia Inferior in AD 197. |
| AD 43 | Lycia | Annexed by Claudius, merged with Pamphylia in AD 74. |
| AD 46 | Thracia | Annexed by Claudius (imperial procuratorial province). |
| AD 47? | Alpes Atrectianae et Poeninae | Created during Claudius' reign. |
| Under Nero | ||
| AD 62 | Pontus | Annexed with Colchis, later incorporated into Cappadocia. |
| AD 63 | Bosporan Kingdom | Annexed into Moesia Inferior, restored as a client kingdom in 68 AD. |
| AD 63 | Alpes Maritimae | Likely became a province under Nero. |
| AD 63 | Alpes Cottiae | Became a province under Nero. |
| Under Vespasian | ||
| AD 72 | Commagene | Annexed to Syria. |
| AD 72 | Lesser Armenia | Annexed to Syria. |
| AD 74 | Lycia et Pamphylia | Merged territories under Vespasian. |
| Under Domitian | ||
| AD 83/84 | Germania Superior | Created by Domitian's campaigns in southern Germany. |
| AD 83/84 | Germania Inferior | Created alongside Germania Superior. |
| AD 92 | Chalcis | Annexed to Syria. |
| Under Trajan | ||
| AD 100 | Territories of Iturea, Trachonitis, Batanea, etc. | Annexed to Syria. |
| AD 106 | Arabia | Annexed without resistance by Trajan. |
| AD 107 | Dacia | Divided into Dacia Superior and Dacia Inferior in 158. |
| AD 103/114 | Epirus Nova | Separated from Macedonia. |
| AD 114 | Armenia | Annexed by Trajan, later restored as a client kingdom by Hadrian. |
| AD 116 | Mesopotamia | Seized by Trajan, later returned to the Parthians. |
| AD 116 | Assyria | Created by Trajan, relinquished by Hadrian. |
| Under Septimius Severus | ||
| AD 193 | Numidia | Separated from Africa Proconsularis. |
| AD 194 | Syria Coele and Syria Phoenice | Divided into two provinces. |
| Under Caracalla | ||
| AD 214 | Osrhoene | Annexed into the empire. |
| Under Aurelian | ||
| AD 271 | Dacia Aureliana | Created after the evacuation of Dacia Trajana. |
- Many of the above provinces were under Roman military control or under the rule of Roman clients for a long time before being officially constituted as civil provinces. Only the date of the official formation of the province is marked above, not the date of conquest.
Provinces of the late empire
[edit]Primary sources for lists of provinces
[edit]Early Roman Empire provinces
[edit]- Germania (ca. 100)
- Geography (Ptolemy) (ca. 140)
Late Roman Empire provinces
[edit]- Laterculus Veronensis (ca. 310)
- Notitia dignitatum (ca. 400–420)
- Laterculus Polemii Silvii (ca. 430)
- Synecdemus (ca. 520)
See also
[edit]- Ancient geography
- Classical antiquity
- Early world maps
- Ecumene
- Geography
- History of cartography
- History of the Mediterranean region
- Latin spelling and pronunciation
- List of Graeco-Roman geographers
- List of historical maps
- Local government (ancient Roman)
References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n "Le province romane" (in Italian). Retrieved 20 November 2021.
- ^ a b Richardson 1992, p. 564.
- ^ Mason 1974, pp. 81, 84–86, 138–139.
- ^ Richardson 1992, pp. 564–565, citing, among others, Plaut. Capt., 156, 158, 474; Ter. Haut., 516; Cic. Cael., 26.63.
- ^ Richardson 1992, p. 565.
- ^ Richardson 1992, pp. 566–567.
- ^ Richardson 1992, p. 567.
- ^ Richardson 1992, p. 570.
- ^ Drogula 2015, pp. 242–245.
- ^ Drogula 2015, p. 247.
- ^ Drogula 2015, pp. 250–51.
- ^ Drogula 2015, pp. 253–254.
- ^ Drogula 2015, pp. 256–257, 263.
- ^ Drogula 2015, pp. 266–268.
- ^ Drogula 2015, pp. 275–276.
- ^ Drogula 2015, pp. 279–281.
- ^ Drogula 2015, p. 292.
- ^ Richardson 1992, p. 573.
- ^ Drogula 2015, p. 298; Richardson 1992, p. 573.
- ^ Drogula 2015, pp. 299–300.
- ^ Brennan, T Corey (2000). The praetorship in the Roman republic. Oxford University Press. pp. 626–627.
- ^ Badian 2012. Formally, the presidency of one of the permanent courts was in fact the provincia of the praetor-president.
- ^ Drogula 2015, pp. 229–330, 341.
- ^ Drogula 2015, p. 304; Richardson 1992, pp. 573–574.
- ^ Drogula 2015, p. 306.
- ^ Pearson, Patricia O'Connell; Holdren, John (May 2021). World History: Our Human Story. Versailles, Kentucky: Sheridan Kentucky. p. 181. ISBN 978-1-60153-123-0.
- ^ Drogula 2015, p. 307.
- ^ Drogula 2015, p. 311. "The use of populär legislation to manipulate provinciae and provincial assignment would also create the armies that brought down the republic".
- ^ Nicolet, Claude (1991) [1988]. Space, geography, and politics in the early Roman empire. University of Michigan Press. pp. 1, 15. ISBN 978-0472100965.
- ^ Hekster, Olivier; Kaizer, Ted. Frontiers in the Roman world. p. 8.
- ^ Eder, W (1993). "The Augustan principate as binding link". Between republic and empire. University of California Press. p. 98.
- ^ Lintott 1999, p. 114.
- ^ Drogula 2015, p. 309.
- ^ Crook 1996, pp. 76–77.
- ^ Drogula 2015, p. 354; Aug. RG 34.
- ^ Drogula 2015, pp. 354–355.
- ^ a b Drogula 2015, p. 355.
- ^ Drogula 2015, pp. 355–356.
- ^ Bowman 1996, pp. 346–347.
- ^ Drogula 2015, pp. 356–57.
- ^ Drogula 2015, p. 364.
- ^ Drogula 2015, p. 370. Drogula also notes that appointing a person of such low status would mean that he would not have the support necessary among the elite to challenge the emperor successfully.
- ^ Drogula 2015, pp. 358–359.
- ^ Drogula 2015, pp. 360–363.
- ^ Bowman 1996, pp. 346, 369–370.
- ^ Bowman 1996, p. 347.
- ^ Bowman 1996, pp. 347–48, noting also that Tiberius regularly remitted embassies from cities in the senatorial provinces to the senate to allow it "an illusion of its traditional functions".
- ^ Nuovo Atlante Storico De Agostini, 1997, pp. 40–41. (In Italian)
- ^ "Note sull'«anzianità di servizio» nel lessico della legislazione imperiale romana" (in Italian). Retrieved 20 November 2021.
- ^ Carlà-Uhink, Filippo (2017). The 'Birth'of Italy: The Institutionalization of Italy as a Region, 3rd–1st Century BCE. Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG. ISBN 978-3-11-054478-7.
- ^ Williams, J. H. C. (2020). Beyond the Rubicon: Romans and Gauls in Republican Italy. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780198153009. Archived from the original on 22 May 2020.
- ^ Long, George (1866). Decline of the Roman republic: Volume 2. London.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Cassius, Dio. Historia Romana. Vol. 41. 36.
- ^ Laffi, Umberto (1992). "La provincia della Gallia Cisalpina". Athenaeum (in Italian) (80): 5–23.
- ^ Aurigemma, Salvatore. "Gallia Cisalpina". www.treccani.it (in Italian). Enciclopedia Italiana. Retrieved 14 October 2014.
Sources
[edit]- Modern sources
- Badian, Ernst (2012). "Provincia/Province". provincia. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acrefore/9780199381135.013.5393. ISBN 978-0-19-938113-5.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - Bowman, Alan K; et al., eds. (1996). The Augustan empire, 43 BC–AD 69. Cambridge Ancient History. Vol. 10 (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-26430-8.
- Bowman, Alan K. "Provincial administration and taxation". In CAH2 10 (1996), pp. 344–70.
- Crook, J A. "Political history, 30 BC to AD 14". In CAH2 10 (1996), pp. 70–112.
- Drogula, Fred (2015). Commanders & command in the Roman republic and early empire. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 978-1-4696-2314-6. OCLC 905949529.
- Lintott, Andrew (1993). Imperium Romanum: politics and administration. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-09375-0.
- Lintott, Andrew (1999). The constitution of the Roman republic. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-815068-7.
- Loewenstein, Karl (1973). The Governance of Rome. Springer. ISBN 90-247-1458-3.
- Mason, Hugh J (1974). Greek Terms for Roman Institutions: A Lexicon and Analysis. Toronto: Hakkert. ISBN 9780888660138.
- Richardson, John (1992). "The administration of the empire". In Crook, John; et al. (eds.). The last age of the Roman Republic, 146–43 BC. Cambridge Ancient History. Vol. 9 (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 564–98. ISBN 0-521-85073-8. OCLC 121060.
- Other sources
- "Early imperial Roman provinces". Livius.org. Archived from the original on 26 December 2016. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- Scarre, Chris (1995). The Penguin historical atlas of ancient Rome. Penguin. pp. 74–75. ISBN 978-0-14-051329-5.
- Großer Atlas zur Weltgeschichte (in German).
External links
[edit]- Map of the Roman Empire in the year 300
- https://web.archive.org/web/20060409205643/http://www.ancientlibrary.com/smith-dgra/